How to start a chess game to win. Endgame strategy or how often to win games? Develop figures to active positions
At first glance, a chess game is very simple. Is it difficult to remember how the pieces move and move them according to the rules? Yes, this is exactly how a beginner or an amateur thinks, who does not yet quite know all the secrets of chess. First you need to get acquainted with the basics of strategy. What rules cannot be violated when playing in the opening, middlegame and endgame. Know the basic principles and direction of a chess game. Let's take a closer look at all of these elements.
Basic principles of chess strategy
Any player who wants to end the game with a victory must follow the following principles of chess strategy:
- analyze and evaluate the position that has arisen on the board
- outline a further plan
- constantly calculate options, and choose the best
Strategy, analysis, plan
Position analysis and evaluation... What is meant. First you need to identify is material equality on the board? (who does not understand what the speech is about, then he should get acquainted with, there is described which figure is how much "costs"). Then the player must assess the position of the kings(both your own and your opponent's), and draw a conclusion whose king is better (that is, he is in the center, under attack, or has already castled). Next you need analyze the position of pawns- whether there are "insulators", passed pawns, connected passed pawns. After that evaluate whose pieces are better... Maybe the opponent has a knight on the edge of the board or a "bad" bishop, or, as my coach called it, a "big pawn" - that is, a bishop that has no squares to move, or has only 1-2 squares, since his own pawns block his way. On the basis of all these conclusions, their totality, an assessment of the position is made, and a decision is made on the further game, building a plan, or fixing a draw.
Plan in a chess game... In order to outline a plan, and not play mindlessly, as beginners do, you need to have more or less already a concept in chess. The book that I recommend everyone to read is Nimzowitsch's book - "". The book vividly describes all the basics of a chess game, without which you simply cannot become a good chess player. The book is very large, in my opinion there are about 500 pages, so you have to work hard to read it.
Most basic principles of strategy and planning can be systematized in the following row:
- Rooks must work on open lines.
- Rooks should rush into the 7th (or 2nd) rank and work along it.
- It is undesirable to move the same piece two or more times in the opening.
- You should not chase pawns, sometimes more important than any piece.
- You need to develop the figures to the center, and not to the edge of the board
- Hit the central pawn, no matter how bad you later (within reason, of course)
This time I would like to tell you something about chess. Many of us know the rules of this game, but usually that's all. That is, a person only knows how each piece moves, and what is checkmate to the king (and that there is a castling is generally known only to a select few).
Not so long ago, I became interested in chess a little more seriously (it became uninteresting to move pieces aimlessly, and even not productive). I flipped through a couple of books on strategy and tactics, played several hundred games and already managed to learn some lessons for myself.
First of all, I must say that if any of you wants to become a professional player, he will have to memorize openings for a long time and tediously (openings are the first moves of the game, during which the pieces are withdrawn and the initial position is taken for a successful attack / defense), various positions of mating the king and other theory.
If you just want to learn how to play chess well (above average), learn just the basic principles will suffice. It is with them that I want to introduce you in this post.
Basic principles of strategy and tactics in chess
1. Be sure to remember the value of each piece:
queen - 9 points
rook - 5 points
elephant - 3 points
horse - 3 points
pawn - 1 point
These numbers are very important to take into account when exchanging pieces. For example, exchanging a knight and a bishop for a rook is unprofitable, and two rooks are predominantly stronger than a queen. However, it is always worth considering the current position. If you have a bishop that simply has nowhere to move because of your own and enemy pawns, change it to a knight or a mobile bishop of your opponent as soon as possible. Especially this refers to the exchange of a knight<->elephant.
2. In the opening, try to develop your pieces as soon as possible (bring them to advantageous positions, from which a large space is "shot through"), and also to occupy the center with pawns. It is better for beginners to start with the e2-e4 pawn for White and answer e7-e5 for Black. I also advise you to learn at least the first 5 moves of the opening of three, four knights, the Hungarian Defense and other openings starting with e2-e4.
3. At the first opportunity (if at the moment there is no aggravated struggle) castling. Castling is done by moving the king two squares to the right or left, and the rook, towards which the king moves, becomes to the left or right of the king, respectively. Castling is possible only if the king and the corresponding rook did not move, there are no pieces between them, and the squares between them are not attacked by the enemy. Also, castling is impossible during the check to the king.
4. Learn to exchange pieces correctly - not only by points. For example, if your opponent has developed a knight by making him 2-3 or more moves, and you have beaten him with a bishop, which until now has not made a single move, such an exchange will most likely be profitable, since you are winning a tempo (in other words, you win in development speed).
5. An exchange can also be beneficial, in which the opponent doubles the pawns (for example, the knight was under the protection of the pawn, after the bishop captures it, the pawn captures the knight and is in front of another pawn). With rare exceptions, double pawns negatively affect the position.
6. Pay close attention to where you place the pieces, where they end up in the exchange process. Try to keep the piece in control of as many fields as possible (the piece controls those fields that are under attack, the field on which the piece itself is located is not controlled by it). So, for example, the knight should not be placed at the edge of the board, and the bishop should not be blocked with pawns. Remember that the knight is strongest in the center of the board, bishops are on open diagonals (the longer the diagonal, the better), and rooks are on open and half-open files (when there is not a single pawn on the way, or only the opponent's pawn).
7. If possible, try to advance your pawns closer to the enemy's camp, this will constrain his position. However, do not forget about protecting the king - if you open it up for check, then you can lose a lot in pace.
8. Try to get passed pawns (which have no enemy pawns on their way or on adjacent files) - remember that this is a big threat for the enemy (a pawn, reaching the end of the board, can turn into any piece), and sometimes a pawn easily connects one of the opponent's pieces, which will be forced to block it.
9. In the endgame (the stage when most of the pieces have already been exchanged) in no case forget about the king - he can easily defend his pieces, attack the enemy and will be a good help in attacking or advancing pawns to queens.
10. Try to think at least one move forward (move is considered a move of a white and then a black piece, that is, two half-moves). If any of the pieces is under attack, immediately count the number of attackers and defenders to find out who will benefit from the exchange if it is captured.
11. After each opponent's move, analyze the change in position - which pieces of yours were under attack, which pieces of the opponent weakened, immediately take appropriate measures. Remember that mindfulness in chess is simply is necessary... By the way, the most common mistake of beginners: they often pay attention only to which figures were hit by a newly emerging figure, but do not pay attention to the so-called. uncovered attack... For example, if the pawn moved and revealed the bishop, which is now attacking the queen.
12. Pay special attention to such combinations and techniques as a fork (attack with a piece on two enemy players at once), an exposed attack (see above), a revealed check (for example, a bishop, attacking a queen, opens a rook, which immediately puts the king in check - so you can pick up the enemy queen), double check, etc. Also, be careful that the enemy himself does not put a fork to you. Knight forks are especially formidable (since in this case it is impossible to close off the attack), in particular on the c7, f7 and c2, f2 squares.
13. Be sure to learn from any position to checkmate (to one king) with a king and a queen, a king and a rook, and, preferably, with two bishops (although such a position occurs quite rarely, and it is very difficult to checkmate here). To do this, watch the video tutorials by Evgeniy Grinis below.
14. Be sure to learn the variations of the "child's mat" and the correct reaction to an attempt to put it (also in the lessons of Evgeniy Grinis).
15. Always consider the current opportunity to check the king - evaluate which pieces can be attacked simultaneously with the check (perhaps some of them are undefended), the possible reaction of the opponent - whether you will win the position or the tempo with the most probable opponent's response.
16. Remember that one of the most powerful techniques in chess is moves that pursue several goals at once, for example, attacking two undefended pieces at once, attack + exposed attack, exchange of an ineffective piece and opening up a castling space, etc. you can win either material, tempo, or both.
That, in general, is all, for a start it is enough. Using these tips, you can easily beat an unprepared opponent, or even compete with someone more experienced.
Still, it's important to understand what to underestimate an experience not in any case. The more games you play, the better you will work out the above principles, the more positions and combinations you will remember (it is not necessary to memorize them, many combinations are remembered by themselves when you play them a sufficient number of times). You can play both with other people and with a computer. It should be noted that it is much more interesting to play with people, because the psychological factor plays an important role here (for example, a person can be set a trap with a bait, but this will not work with a computer).
For those who want to go a little deeper into the study of chess, I am posting two textbooks by Yasser Seirawan - one on strategy, the other on tactics.
Video tutorials from Evgeniy Grinis
Chess for beginners. Fundamentals of Chess 1. The rules of chess. Comparative value of chess pieces
Chess for beginners. Chess Fundamentals 2. Checkmate to the Lonely King
Chess for beginners. The computer plays without a queen and two rooks
Chess. Theory of Debuts 1. Defense of Philidor, Debut of Ponziani
Information from the sponsor
Friend Around: a popular messenger. Now it has become possible to install the Friend Around program on a computer running the Windows operating system.
The goal of a chess game is to checkmate your opponent.
Checkmate occurs when the king is attacked by another piece and has no way of avoiding the attack. This is where the game ends. However, mate requires preparation.
To win a game of chess, the following six rules must be followed:
1. Make Sure Moves in the Opening
The goal of your first moves is to gain control of the board. The most important part of the board is the center. If your pieces and pawns control the center, you can dictate the direction of the game. In the position below, White's two pawns have excellent control over the center of the board, while Black has no influence.

2. Don't Give Shapes Just Like This
Exchanging pieces is common in chess, however you should only exchange pieces of equal value. Many players lose because they simply give up their pieces and pawns for free. In this case, you need to take all the pieces that your opponent gives you for free (just beware of traps).

3. Bring Shapes to Active Positions
Before you can get to the king, you need to put your pieces in position to attack. This means that when attacking, you need active pieces that have a lot of possibilities.
Pawns control cells. Horses love to be in the center. Elephants love long diagonals. Rooks like to roll out to the center or occupy open lines. Your queen should be ready to join the fight.

4. Coordinate the Attack on the King
Usually one piece cannot be mated. This requires the joint work of several figures. Most often, you will need a piece that will check the king, and at least one piece that will defend your attacking piece so that the king cannot take it. Sometimes you even need to sacrifice a few pieces in order to break the opponent's defense.

5. Watch Your King's Safety
Sometimes players are so focused on the opponent's king that they simply forget about their king. Remember that your opponent is also playing and will also attack your king. Be sure to watch out for the threats that your opponent creates when making the next move. One of the best ways to protect your king is to place him behind a row of several pawns that will protect him. In the position below, the white king is comfortable and safe, and the black king can be easily attacked.

6. Always Be Polite
Whether you win or lose, always congratulate or thank your opponent for playing. Wins, like losses, are part of the game. Even the best players in the world often lose.
Therefore, be kind and grateful even when you fail, and after the game, just think about how you could play better next time.

Playing chess for beginners is not an easy task. More often than not, chess for beginners is presented as fun and enjoyable pastime. To learn to play really well, you have to take it seriously. It is necessary to spend a lot of time both on the study of theory and on the consolidation of knowledge in practice.
One way or another, every person who respects this game should know the general concepts of strategy, tactics and basic combinations.
Strategy and tactics in chess
For beginners, tactics play a key role in the game of chess. Basic techniques: double hit, fork, pin, exchange, sacrifice. It is worth saying that attack, defense and even move are also tactical techniques.
Let's take a look at the least obvious ones.
This is a project for beginners, approved by our readers, in which you or your child can improve the skill of the game, complete a chess rank, and in a short time grow to the prize-winner of regional tournaments. The teachers are FIDE masters, online training.
Double punch.
A situation when one piece is attacked by several enemy.
Example:
Starting position. White's rook is under attack from a pawn.

White to move. The black pawn is under attack by the white rook and bishop.
So, a double hit occurs when a piece makes the attacker and another. In this case, the rook made the bishop an attacking piece.
Fork.
It is a type of double strike. The difference is that forks guarantee the loss of at least one enemy piece.

The black knight put a fork. White is guaranteed to lose a rook.
Bundle.
A situation in which one or more pieces are at a disadvantage to attack.

The white king is attacked by the rook. In this case, the white knight cannot take the rook, because the king will be under attack by the bishop: such a move is prohibited by the rules. White's knight is “tied”.
Exchange... A move in which both players lose one piece: exchanged.
Victim... A situation when a player deliberately concedes one or more of his pieces. A very important technique, used as a distraction.
Basic combinations and pitfalls in chess
A successful chess game for beginners requires knowledge of the basic types of combinations: overlap and block. Traps like these will allow you to win a lot of opponents at the initial stage.
Overlapping.
The essence of this winning combination is to interrupt the connection and deprive the opponent's pieces of maneuver.
Consider the situation:

The black king is well protected by the queen and bishop.
White makes an unexpected move:

At this point, black resigns. Why? The fact is that the rook move completely limited the possibilities of the enemy queen and bishop.
Two cases are possible:
1. Black takes the rook with the queen.

2. Black takes the rook with his bishop.

In both cases, the enemy queen was blocked and stopped defending the king.
Blocking.
The essence of this combination: attracting an enemy figure in order to deprive it of space. With this combination, it's easy to checkmate.
Everything will become clear with an example:

The black king is cornered. White's goal is to deprive him of the a7 square and checkmate with the knight.
White to move:

Black has no other option but to take the knight with the bishop.
Having deprived the king of the move to a7, White can easily checkmate with the knight:

Outcome
We have reviewed the basic chess combinations and tactical techniques. As a bonus, we suggest watching a video on the topic.
It is also known that information does not linger in the head without practice. It's time to play chess, consolidating the knowledge gained in a real game!
Below you can watch a video lesson of playing chess
Chess for beginners video
What do you need to do to win?
The goal of a chess game is to checkmate your opponent.
Checkmate occurs when the king is attacked by another piece and has no way of avoiding the attack. This is where the game ends. However, mate requires preparation.
To win a game of chess, the following six rules must be followed:
1. Make Sure Moves in the Opening
The goal of your first moves is to gain control of the board. The most important part of the board is the center. If your pieces and pawns control the center, you can dictate the direction of the game. In the position below, White's two pawns have excellent control over the center of the board, while Black has no influence.
2. Don't Give Shapes Just Like This
Exchanging pieces is common in chess, however you should only exchange pieces of equal value. Many players lose because they simply give up their pieces and pawns for free. In this case, you need to take all the pieces that your opponent gives you for free (just beware of traps).

3. Bring Shapes to Active Positions
Before you can get to the king, you need to put your pieces in position to attack. This means that when attacking, you need active pieces that have a lot of possibilities.
Pawns control cells. Horses love to be in the center. Elephants love long diagonals. Rooks like to roll out to the center or occupy open lines. Your queen should be ready to join the fight.

4. Coordinate the Attack on the King
Usually one piece cannot be mated. This requires the joint work of several figures. Most often, you will need a piece that will check the king, and at least one piece that will defend your attacking piece so that the king cannot take it. Sometimes you even need to sacrifice a few pieces in order to break the opponent's defense.
5. Watch Your King's Safety
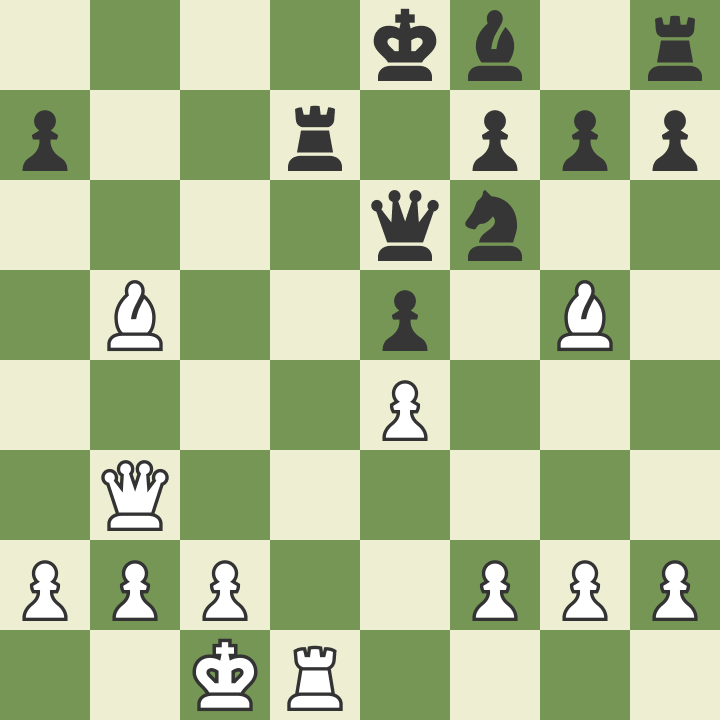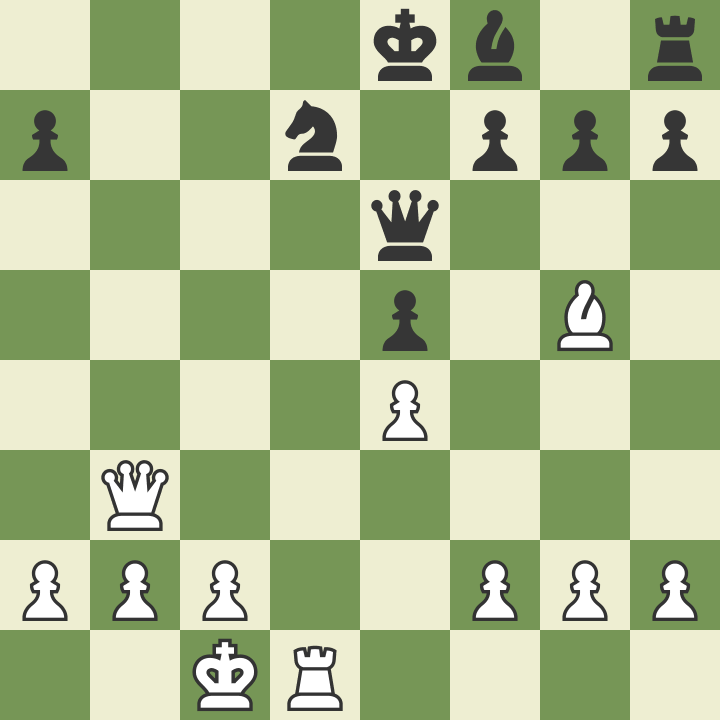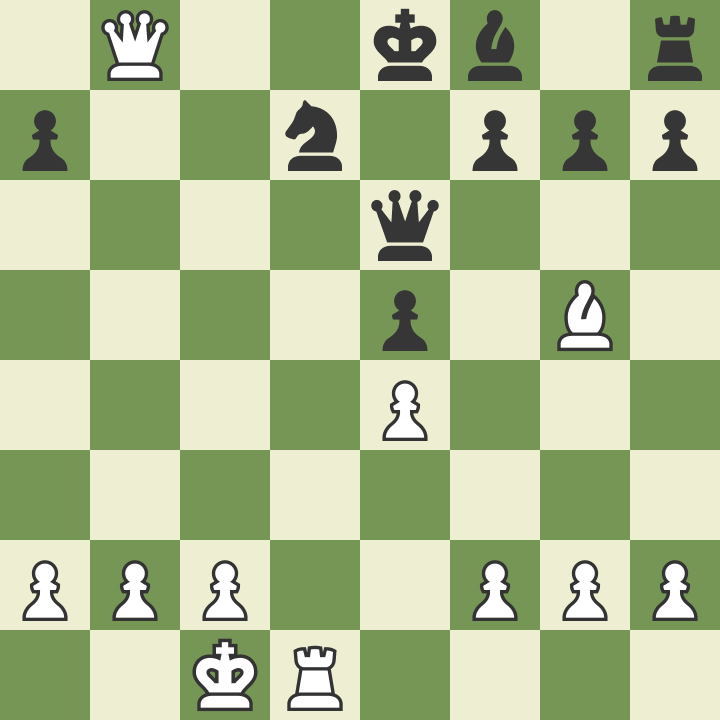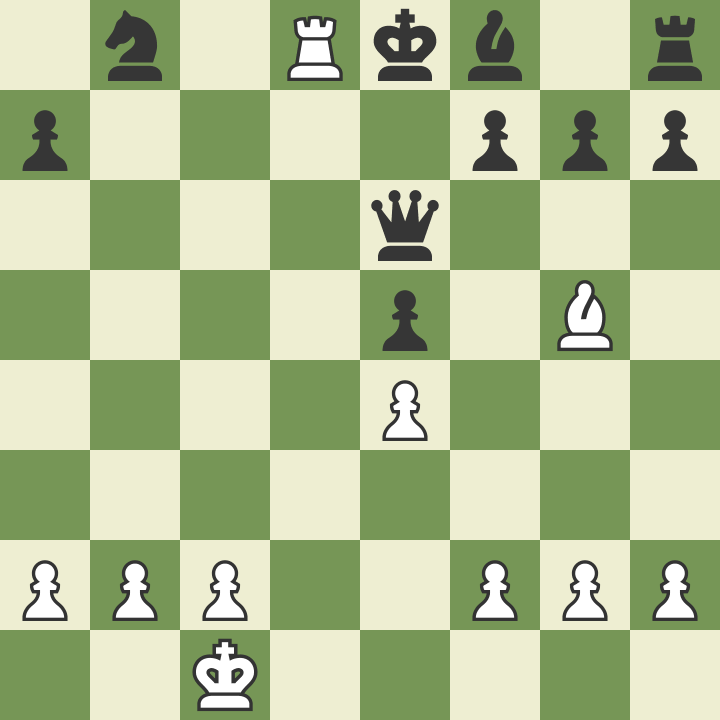
Sometimes players are so focused on the opponent's king that they simply forget about their king. Remember that your opponent is also playing and will also attack your king. Be sure to watch out for the threats that your opponent creates when making the next move. One of the best ways to protect your king is to place him behind a row of several pawns that will protect him. In the position below, the white king is comfortable and safe, and the black king can be easily attacked.

6. Always Be Polite
Whether you win or lose, always congratulate or thank your opponent for playing. Wins, like losses, are part of the game. Even the best players in the world often lose.
Therefore, be kind and grateful even when you fail, and after the game, just think about how you could play better next time.

For even more tips and tips on how to win at chess, sign up to the site. It's easy and free!


 Lures in Pokemon GO: about the features of the application Where to get lure modules to attract Pokemon
Lures in Pokemon GO: about the features of the application Where to get lure modules to attract Pokemon Cool nicknames for fortnight
Cool nicknames for fortnight Primal World with Stonies Primal PC Games
Primal World with Stonies Primal PC Games Endless War - play online
Endless War - play online